Apps are becoming a reliable way to deliver content and service. But is it possible to achieve success in an extremely competitive environment, and how can you do it?
There are few applications for users. Total app downloads are expected to reach 200 billion by 2019. Last year, $ 3 billion was spent on ads to boost installs, up 80% from a year earlier.
Apps are an opportunity to build mutually beneficial relationships with loyal customers. Getting users to find and install an app is a daunting task for mobile app developers and brand marketers, but that’s not all. According to statistics, 25% of users open the application only once and do not return to it.
People interact with their phones, spending valuable time on them, so UX should be as effective as possible.
Google worked with Answer Lab to conduct research involving more than a hundred people to get their opinions on hundreds of different applications, from categories such as e-commerce, insurance, travel, ordering food, ticketing and services, and financial management (apps for games, social media, and music services were not included in the study).
The tasks focused on conversion were studied: ordering, booking hotel rooms, among other things, tariff plans and prices were taken into account Android App Development Company Services
Based on the results of the research, you can draw up a guide to creating convenient and practical functionality, a key component of a good user experience and good design of mobile applications.
Basically, building an engaging app starts with usability.
Chapter 1: Navigation
Users need to help them quickly find the content they are looking for.
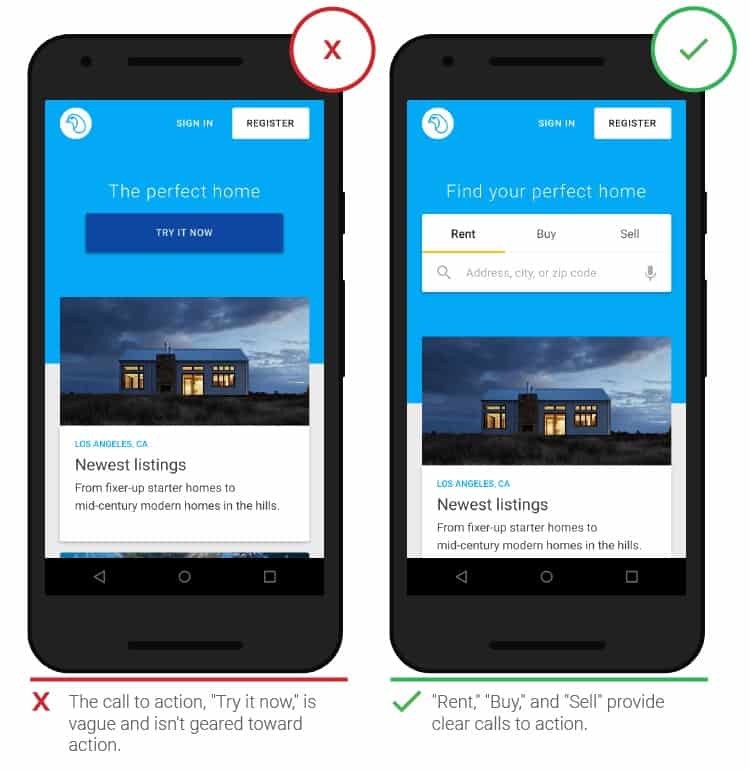
- It is necessary to demonstrate the usefulness of the application
Assignments should be clearly defined, and CTAs should be present at the top center of the screen. It is better to make the main and new details of the interface more visible against the background of other design elements, so that they can interest users and not cause disappointment.
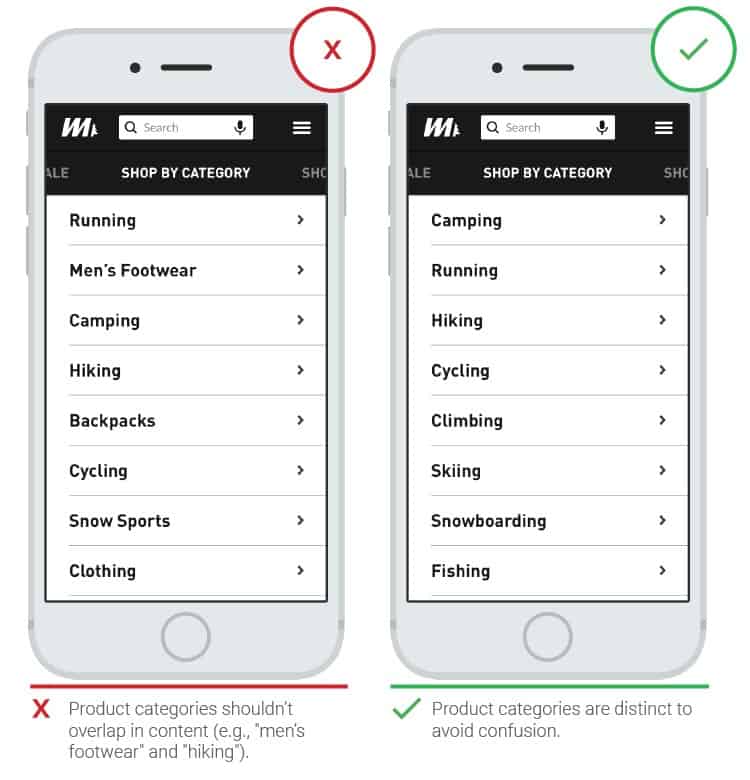
- Menu categories and selection of corresponding names
It is difficult for users to understand the purpose of menu categories that differ from the familiar model. Categories should be easy to understand and not contain overlaps. This is especially important in cases where the user, after a series of unsuccessful searches, turns to the menu as a last resort.
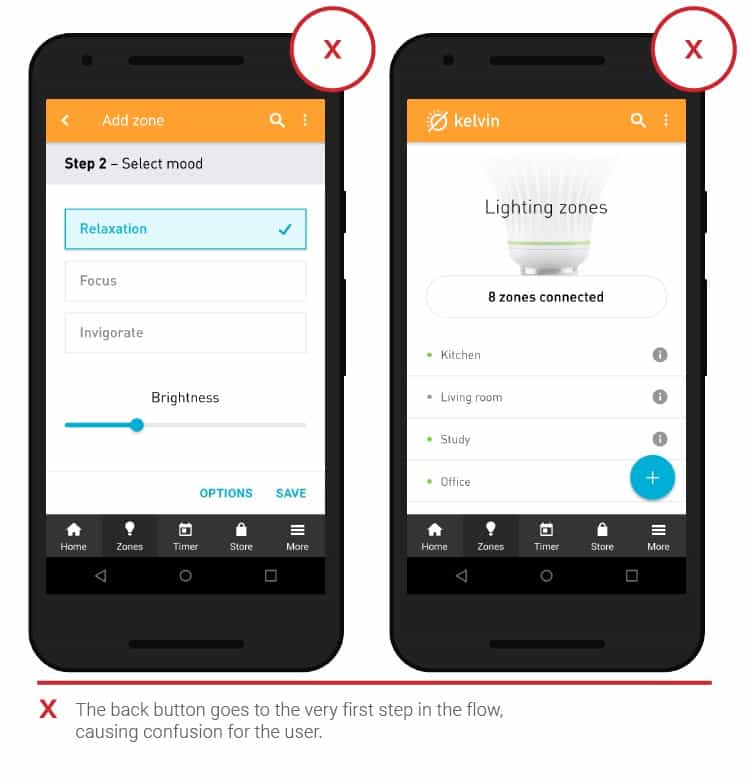
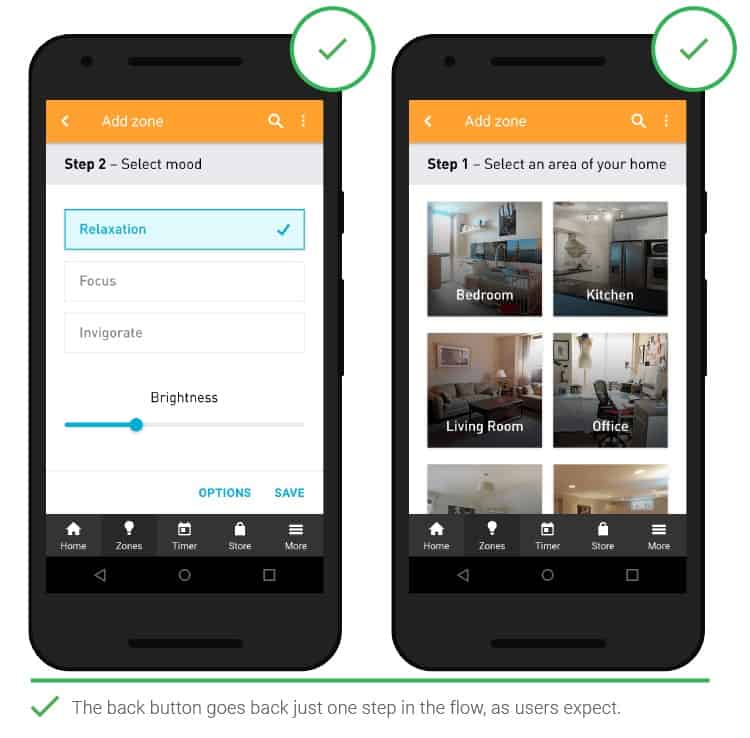
- Back button
Returning to the previous screen of the application should be done in one step so that users do not have to start all over again, from the main screen, which in some cases leads to the loss of unsaved data. Let people go back with one click, so you don’t have to resort to workarounds. Visible navigation aids increase the likelihood of conversions.
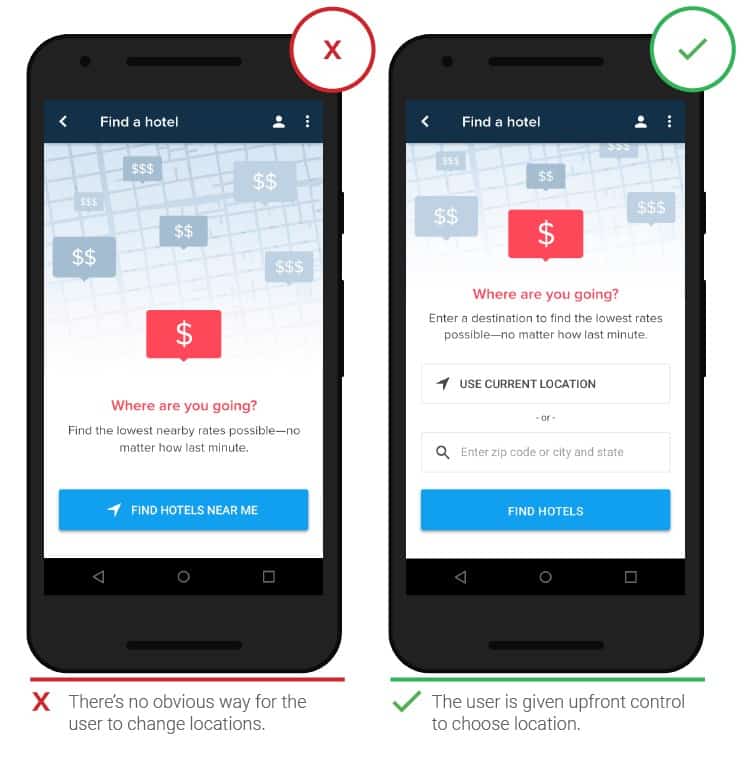
- Changing your location manually
Automatic location discovery will save users time. However, sometimes it becomes necessary to find stores that are far away, so manual entry should be simple and straightforward.
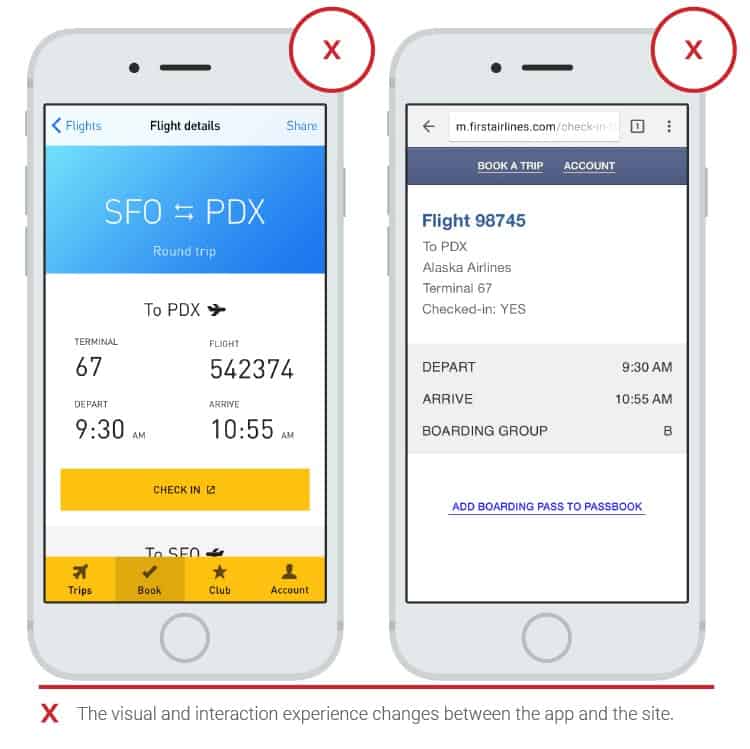
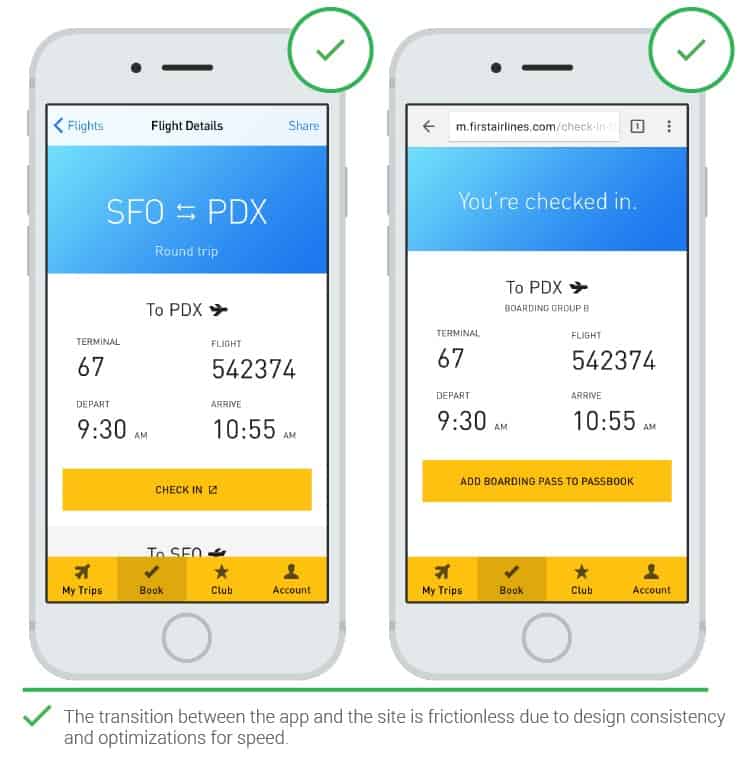
- Transitions between mobile and web applications
If an app is redirected to a web app to show more content or to complete a specific task, this can be inconvenient. Especially when the look or feel of the design of the two platforms is too different. Transitions often slow down and you have to wait for the web page to load. If you can’t do without transitions to web applications, then at least the design should look holistic. And, of course, it’s better if the transition is fast.
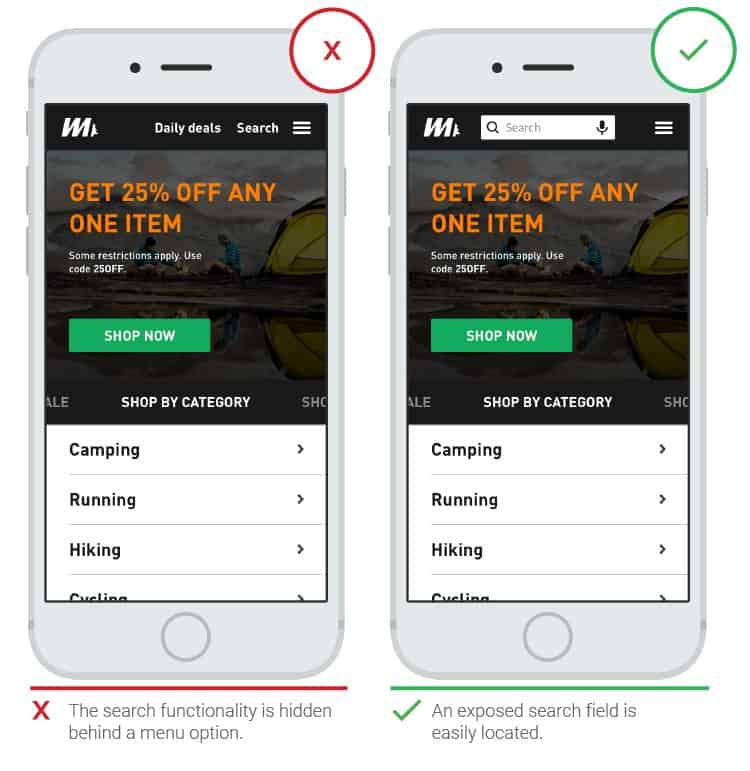
Chapter 2: App Search
Functional search is extremely important because it allows you to find what you are looking for. The principles below will help you make your search as efficient as possible.
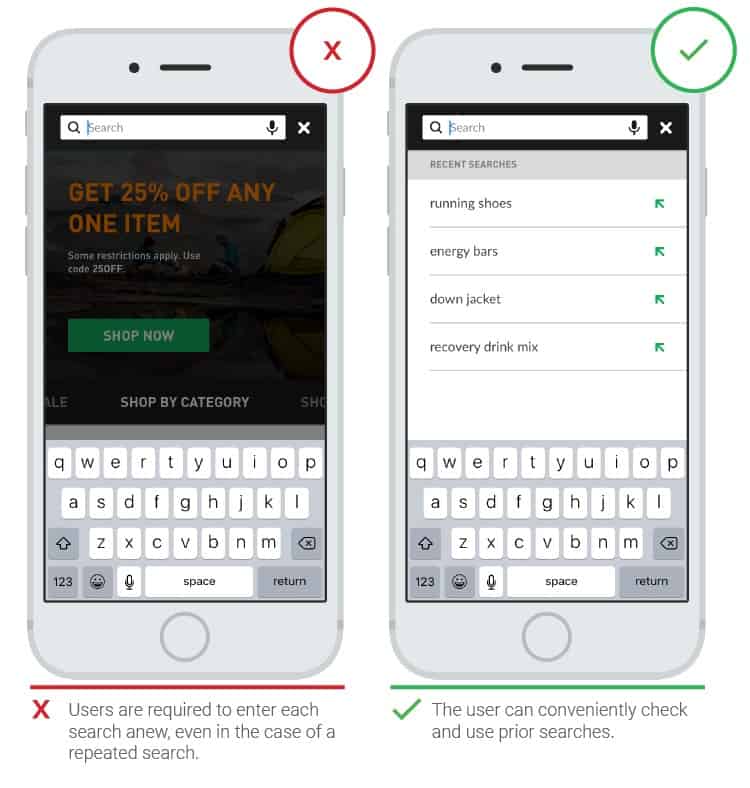
- Noticeable search bar
Those looking for something specific tend to look for a search string. This feature is often preferable to browsing through available topics.
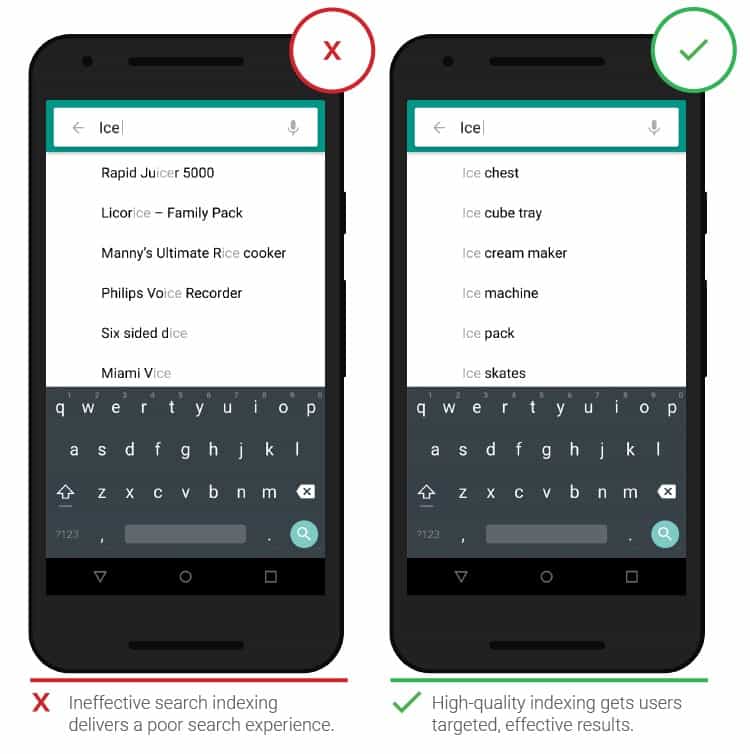
- Functional search
People expect in-app search to function the same as Google. Automatic spelling corrections, root word recognition, intuitive typing, and typing hints – all of these tools reduce the chance of errors, speed up searches, and help users convert.
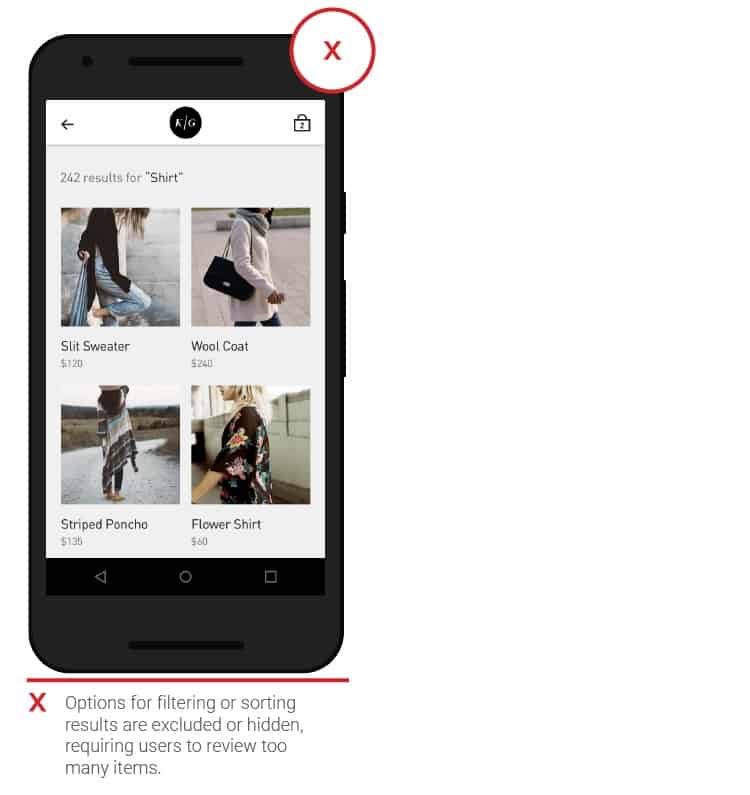
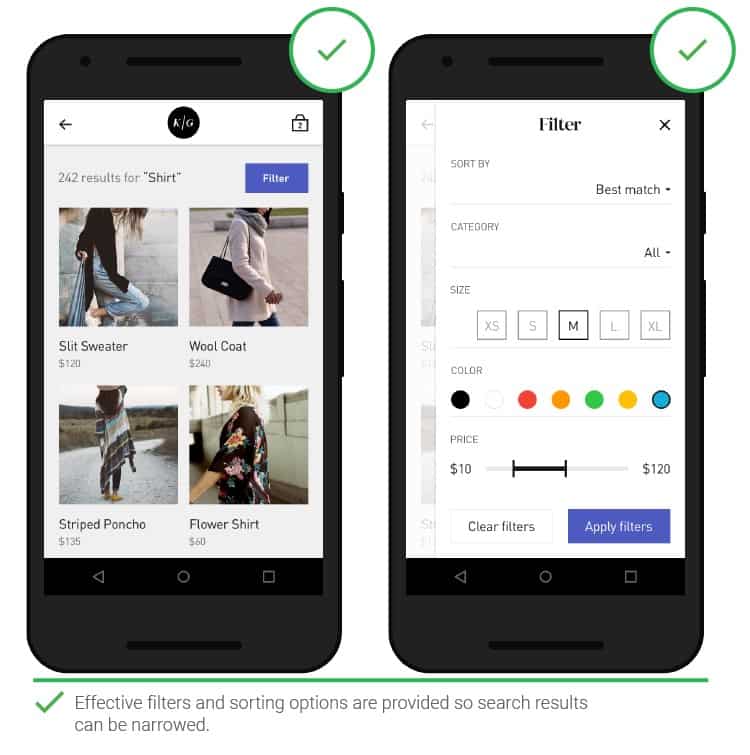
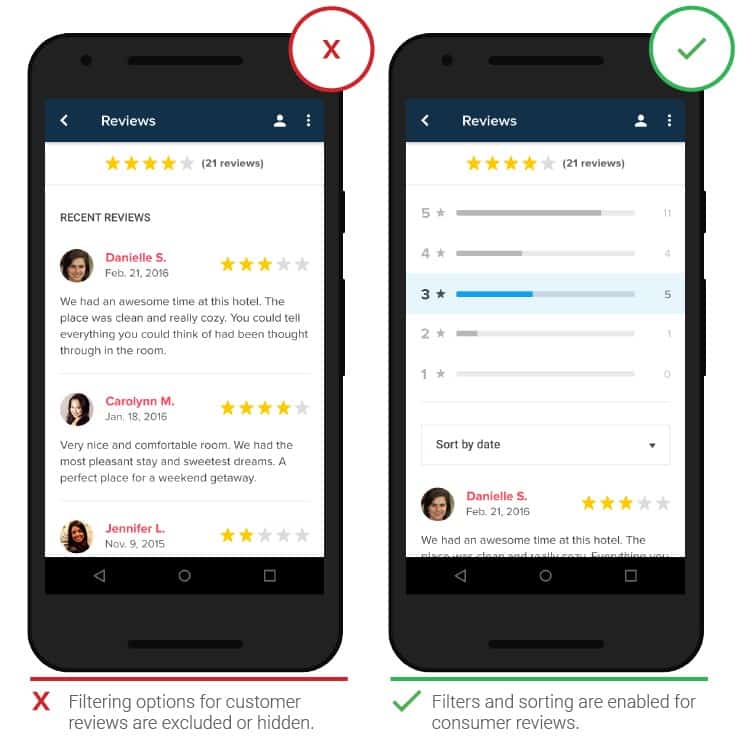
- Filters
People get frustrated when the search results don’t match the query and / or when the search comes up with too many results.
Filters and other options can help reduce the number of options and sort the results, which would require an excessive amount of scrolling on a small screen.
Chapter 3: Commerce and Conversions
As mobile commerce develops, people will be more demanding about the functionality of finding, browsing and purchasing products.
- Recent purchases
By making your past and recent purchases available, you save time and effort for the person who installed the app. This nuance is especially relevant for popular applications, in which repeat purchases are often made.
- Reviews and ratings
Reviews are important and are part of the buying process. A large number of reviews will help dispel the doubts of a potential buyer regarding a particular product. The overall rating, which is based on a combination of positive and negative reviews, makes it possible to get an idea of the product and find out its “real story”. Provide an opportunity to read the most recent, most positive, and most negative reviews. It is recommended to show reviews from verified buyers, those who have already made purchases, so that there is no doubt about the authenticity of the reviews.
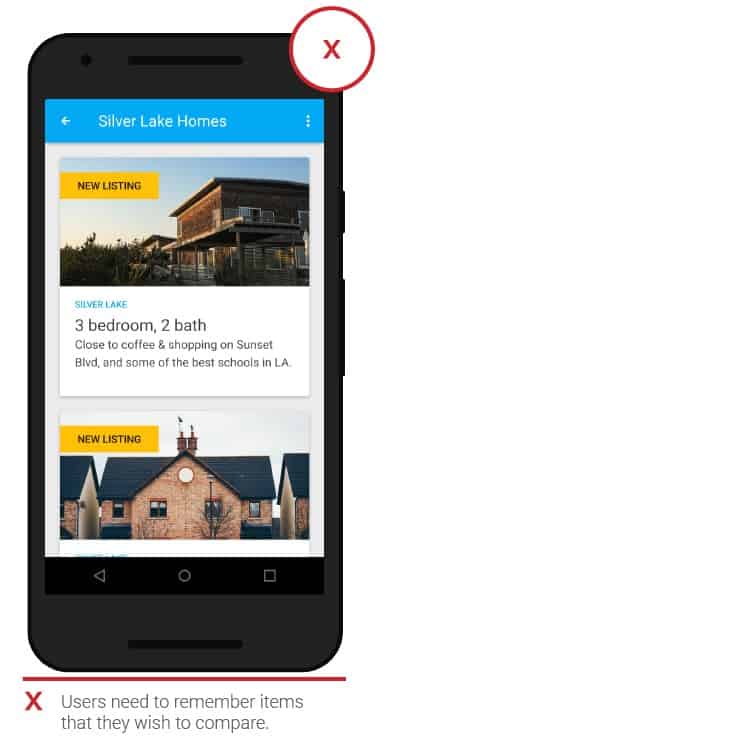
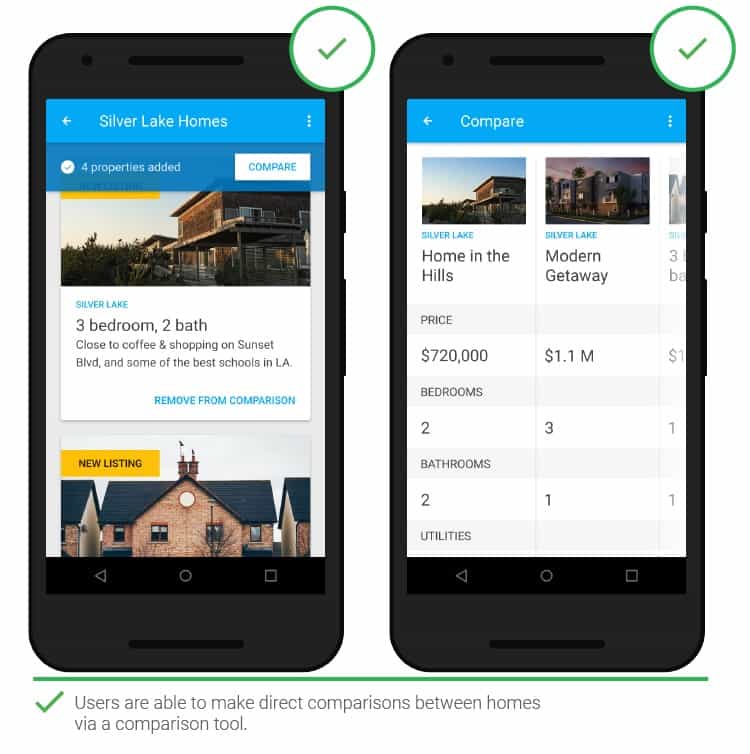
- Product comparison
You may need a simple and efficient way to compare items of interest. Without this option, you would have to put items in the cart, or remember certain products and come back to them later. In a desktop browser, things are simpler – you can open multiple tabs. The in-app comparison option will significantly speed up the purchase.
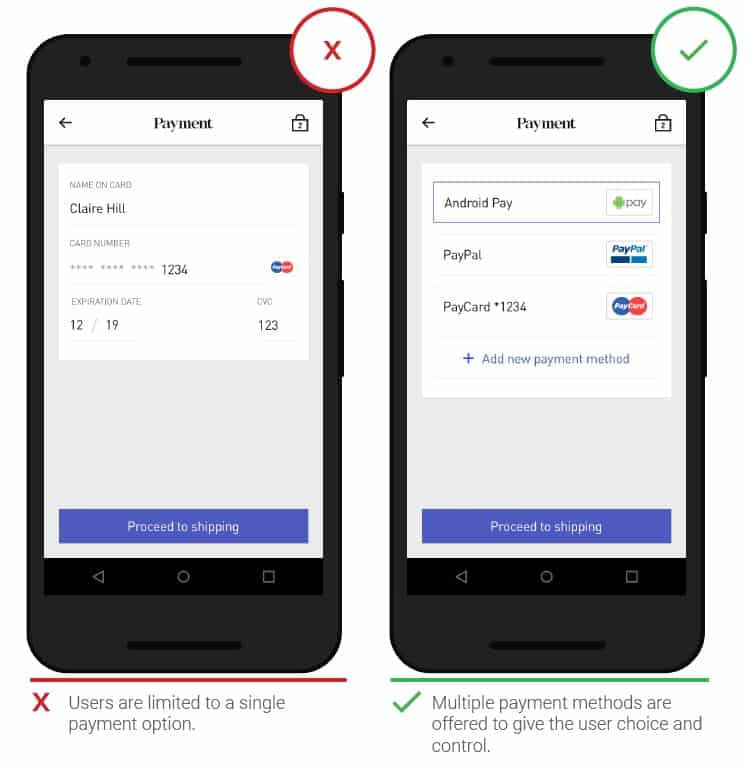
- Multiple payment methods
In those applications where alternative payment methods are implemented (PayPal, Apple Pay and AndroidPay), there is no need to fill out additional forms during payment.
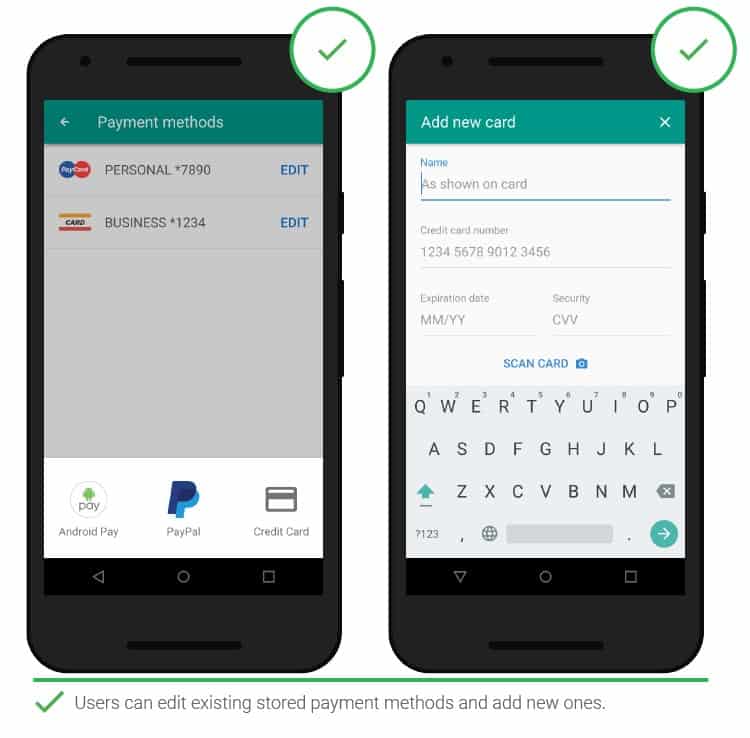
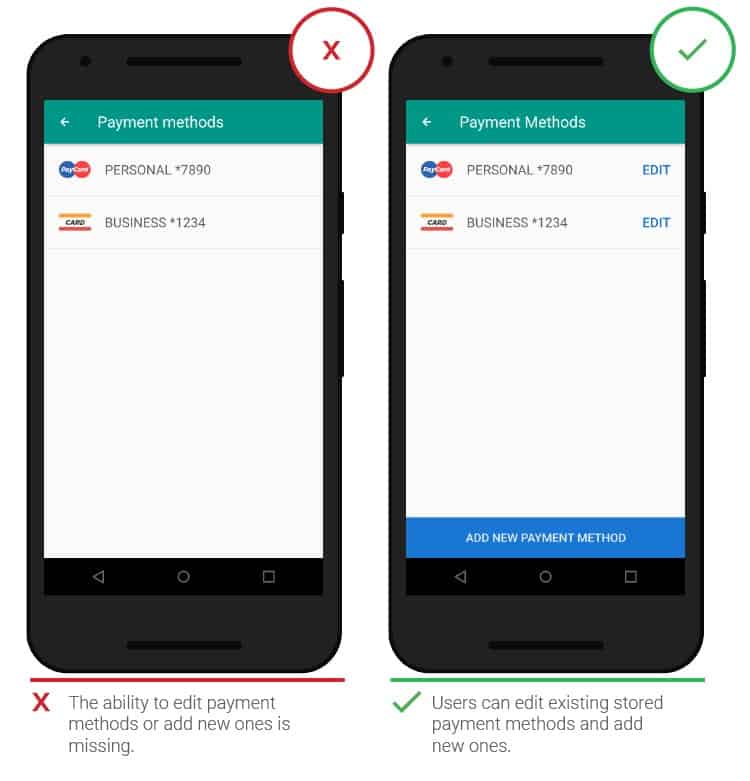
- Adding payment details
It is worth simplifying the way you save your payment details and reducing the number of steps required. Create simple payment card entry pages with additional options such as card scanning. The ability to add multiple cards, as well as the function of switching between them, will not be superfluous.
Chapter 4: Registration
It’s a way to connect with the user and improve conversion rates. But at the same time, registration is often associated with a number of difficulties and inconveniences that hinder conversion. This chapter will describe the registration process through which users can quickly navigate to the desired sections of the applications.
- Offer to register
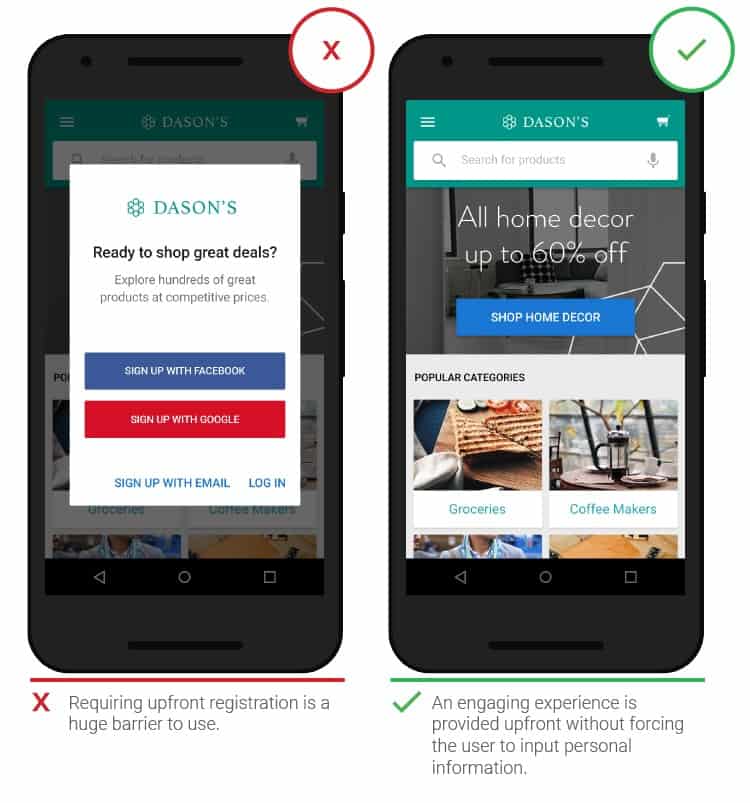
People often close applications that immediately ask for personal information; exception: situations when the desired result is not long in coming (ordering food, taxi). This is especially true for apps from brands that are not widely used, or apps whose benefits are difficult to draw immediately upon. It seems advisable to ask a person to register only if you cannot do without it. Guest purchase is a practical example of this principle.
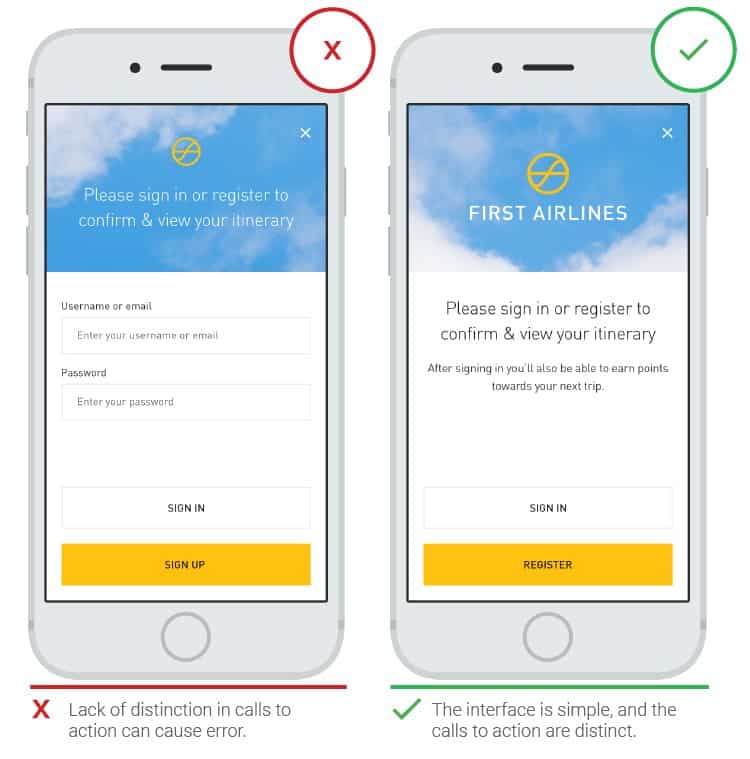
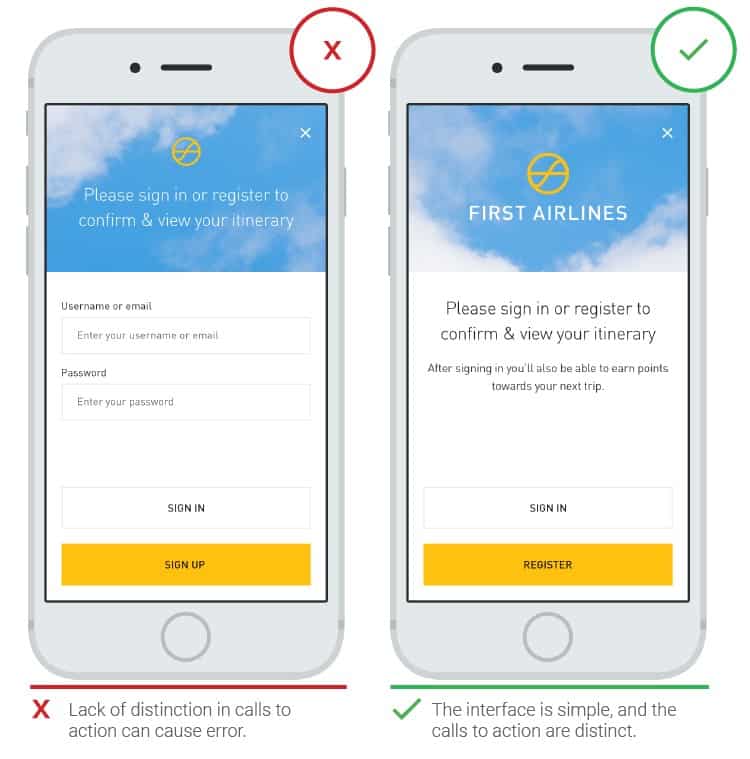
- Difference between “sign in” and “sign up”
Many clients commit the wrong action by trying to register by clicking on the “sign in” button, after which a password field appears. This is because people quickly scan the screen and click on the first call-to-action item they see. The design of the “sign in” and “sign up” buttons should be different.
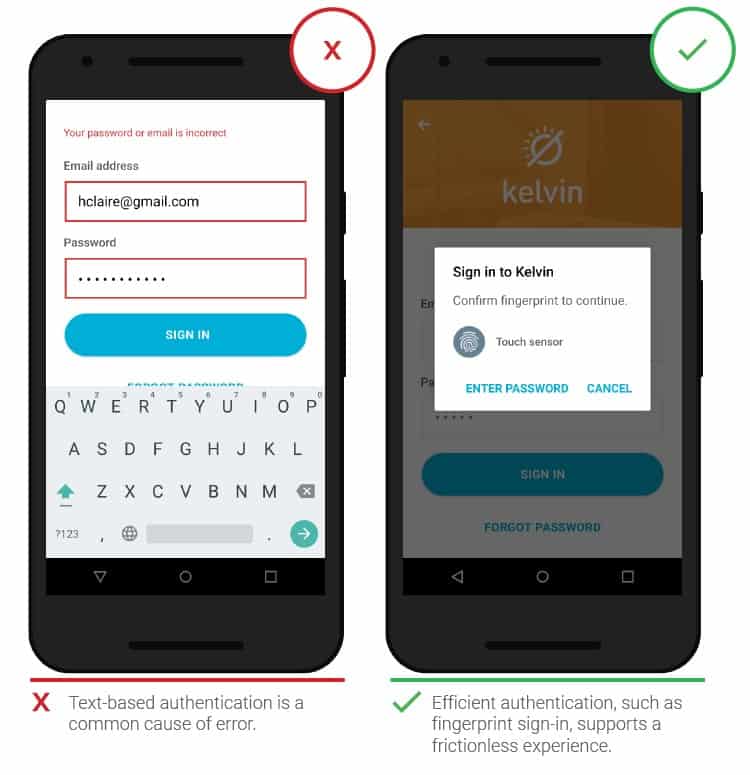
- Password confirmation
People lose their temper when they have to go through the complex, multi-step process of creating or recovering a password. Simplifying the confirmation procedure reduces the failure rate. Minimize the number of steps required, or use alternative authentication methods (login through third-party services or fingerprint).
Chapter 5: Data Entry Forms
Forms are extremely important and should be completed quickly and without unnecessary complexity.
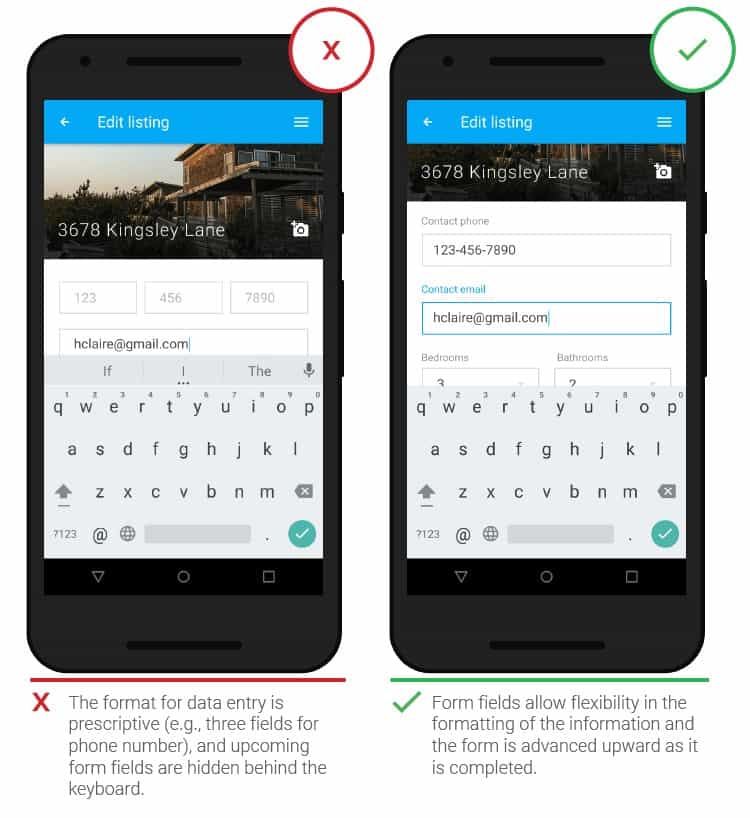
- Form design
Form design should provide a way to enter data, and application screens should be designed to support multiple input formats so that people don’t have to adapt to existing constraints. You should also make sure that the data entry fields are visible and not obscured by other interface elements such as the keyboard. Empty fields must be raised up to be visible. Features such as autocomplete, auto-capitalization, and credit card scanning are also included.
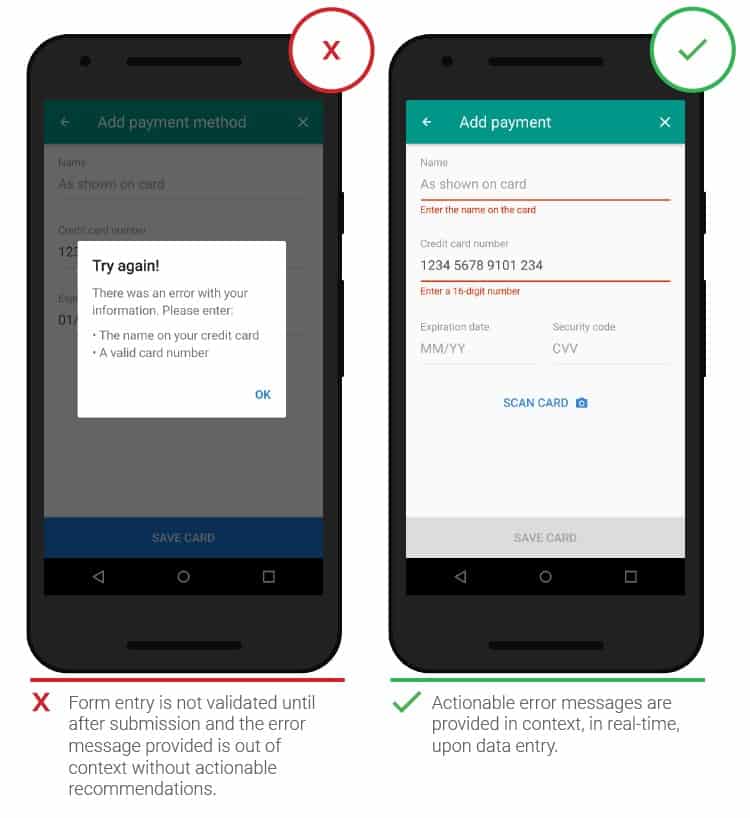
- Real-time error messages
No one likes it when, after filling out the form, a message appears that there was a mistake somewhere. It is better to highlight errors in real time so that you do not have to repeat everything from the beginning. User experience testing will eliminate possible unwanted consequences. You can use this Error Fix method.
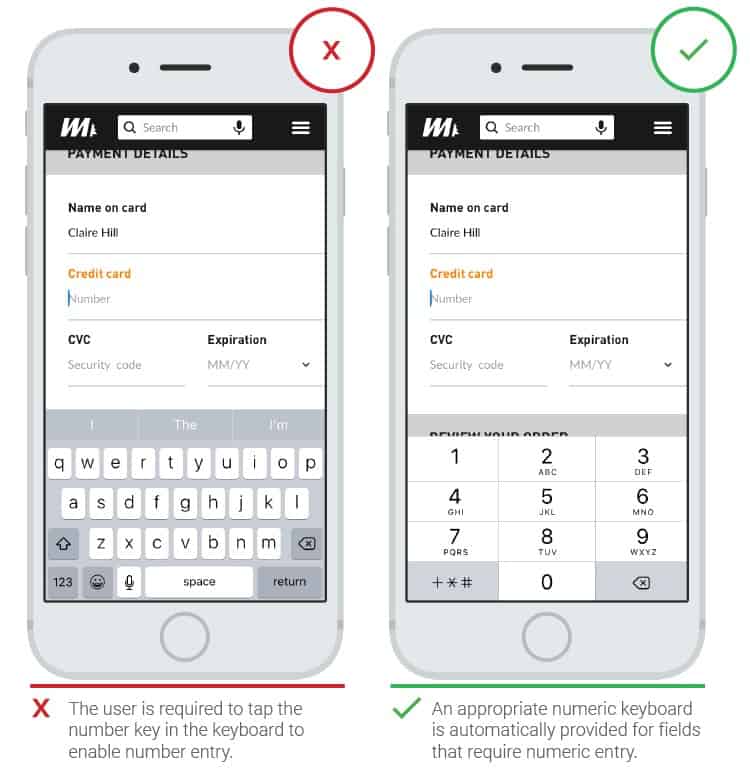
- Keyboard
Smart keyboards are appreciated by users. In applications, this UX element should be implemented consistently, and not only for specific tasks.
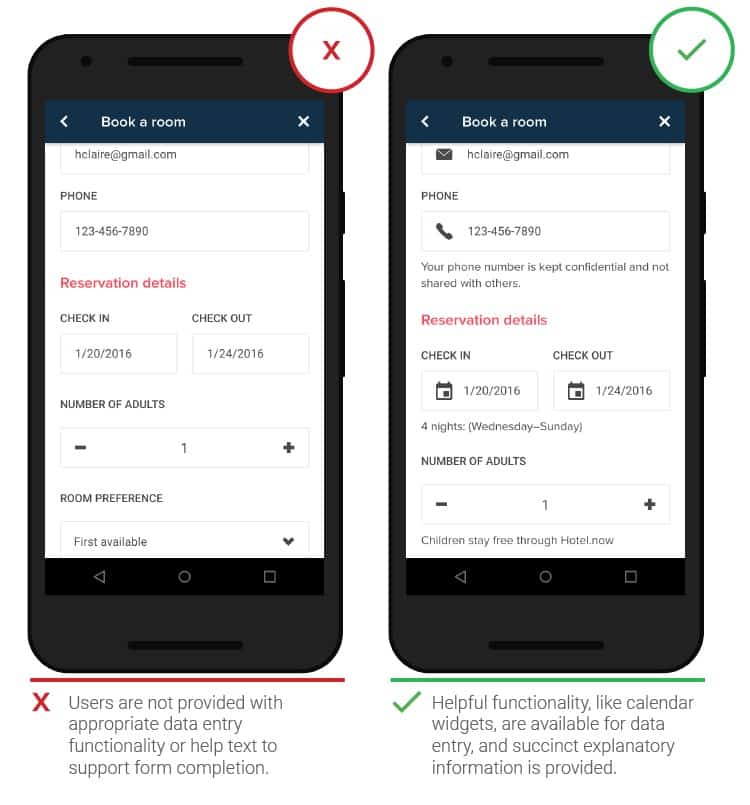
- Supporting information in forms
Aids may be appropriate in the form. For example, if you need to enter a specific date, a tool such as a calendar will be useful to quickly select a suitable day and not go into the smartphone’s calendar.
Chapter 6: Usability
Specific approaches to solving design issues will provide quality UX.
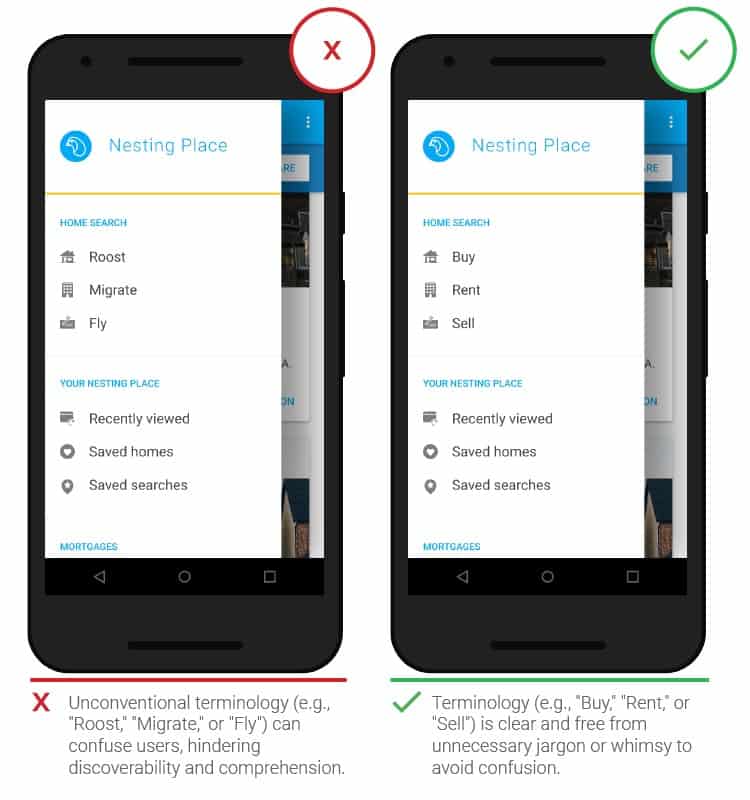
- Friendly names
Unfamiliar terms or phrases increase the cognitive load on users. When CTA elements are labeled with specific terms or working names that are mostly used within a particular brand, people uninitiated in nuance may not understand them. Accessible names and functionality are a kind of competitive advantage.
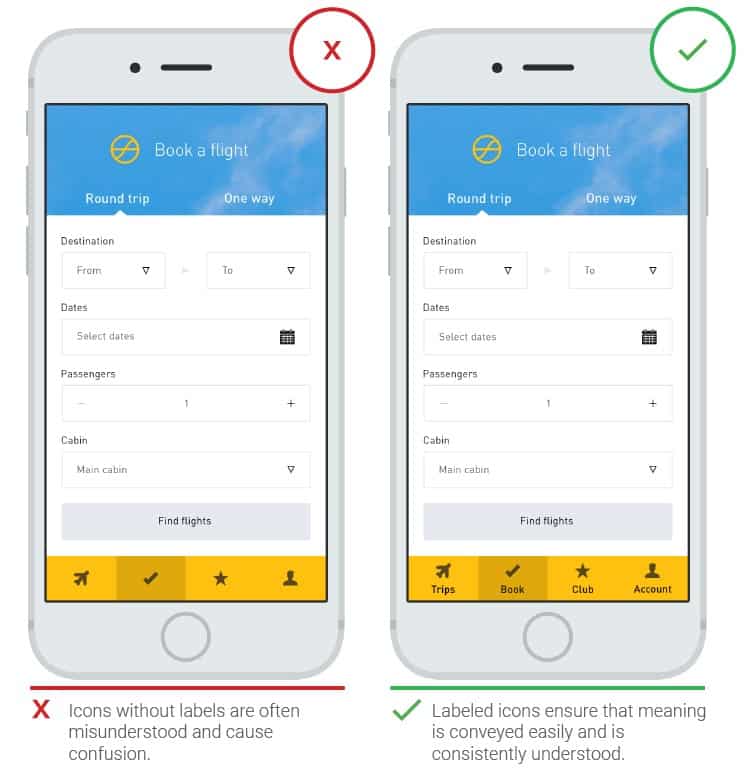
- Titles and visual cues
Clear titles are required for visuals and iconography. Google research shows that not all apps have a menu, cart, account, or store finder with universal icons. The same goes for all kinds of filters or sorting functions. A person is more likely to click on an icon with a name than an icon with only one icon.
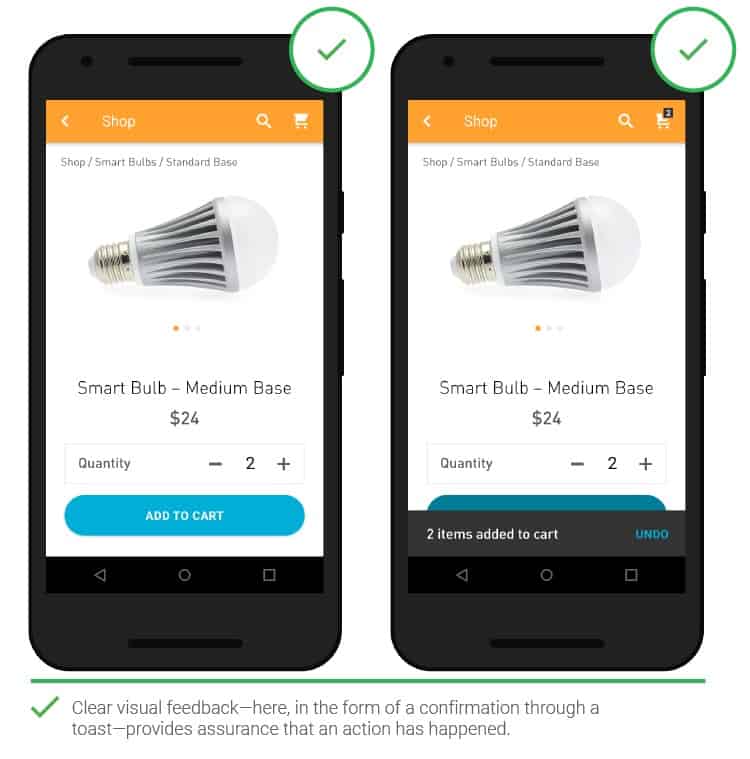
- Feedback
When adding products to your cart or placing an order, feedback omissions may raise doubts as to whether the request has been processed. These doubts will be dispelled by animation and other visual elements.
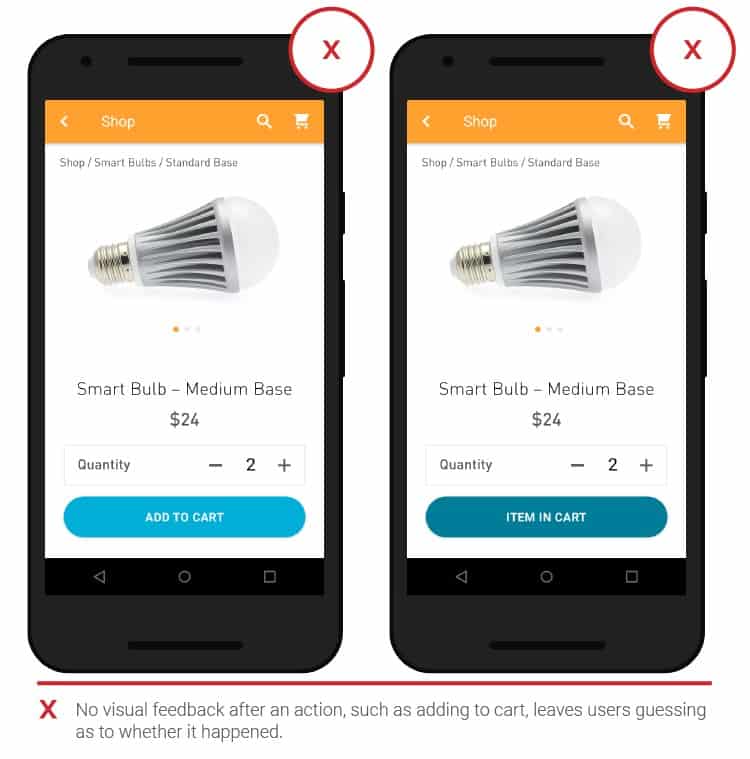
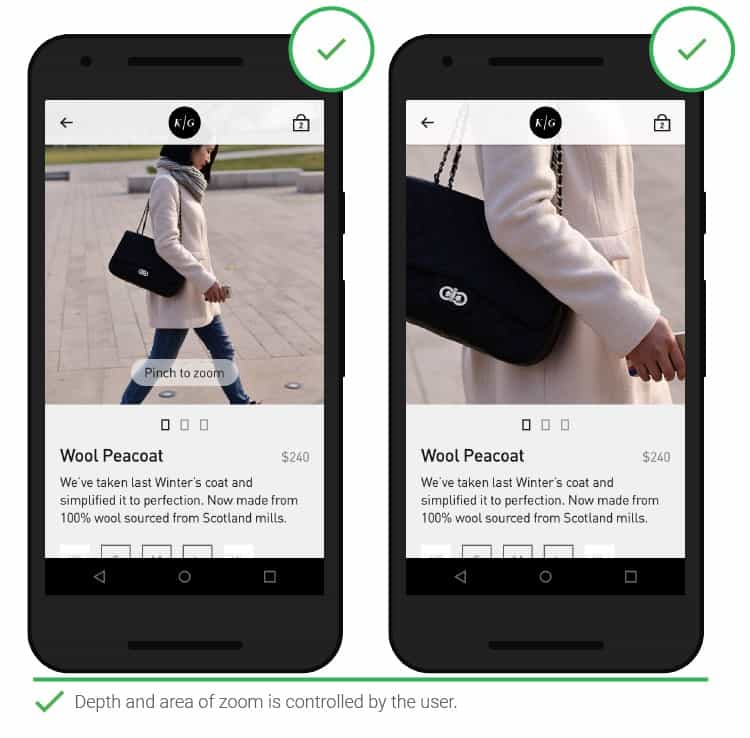
- Scaling
People need the option to zoom in when viewing images. The maximum close-up level provided does not always suit everyone. There are frequent cases when only a separate part of it can be seen on an enlarged image. Give people the ability to zoom in as much as necessary.
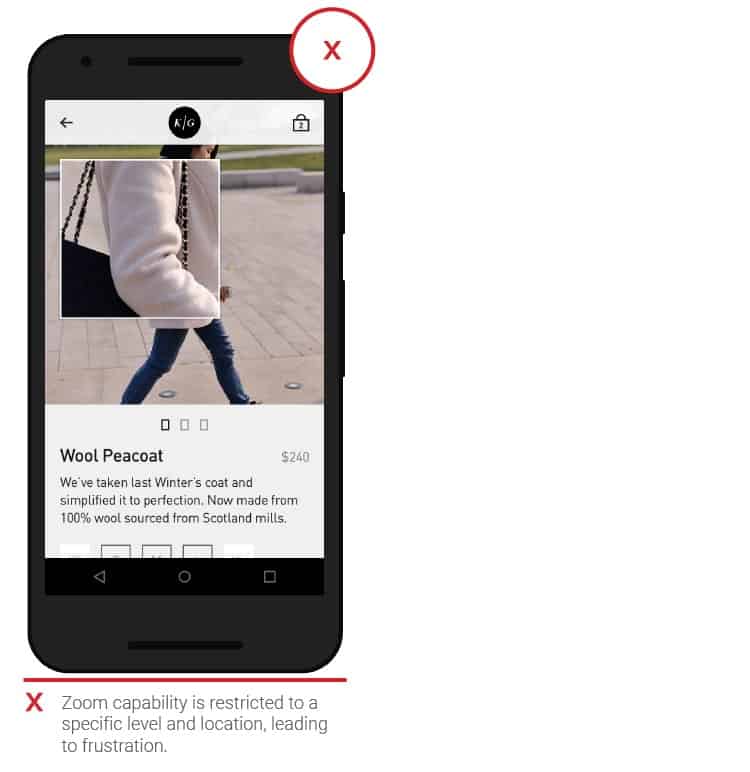
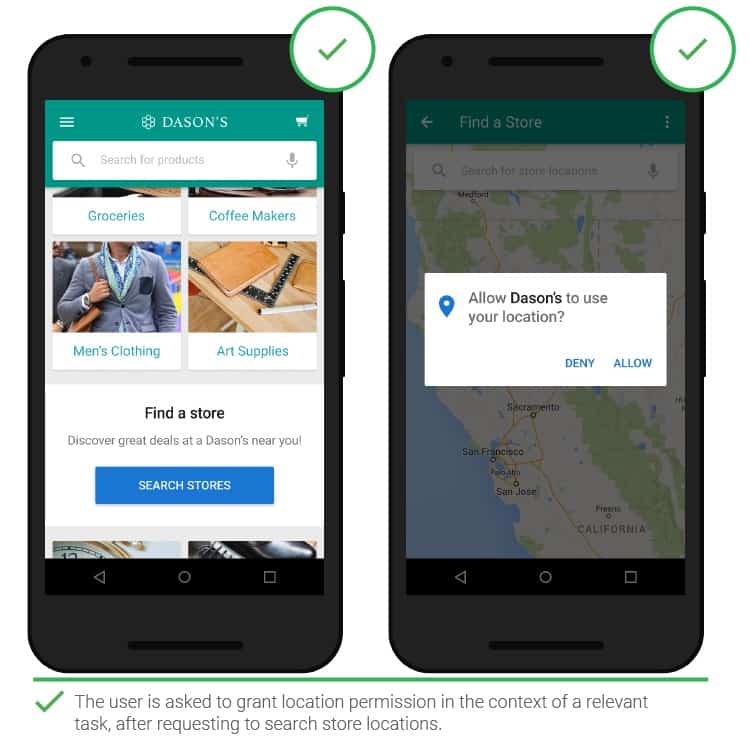
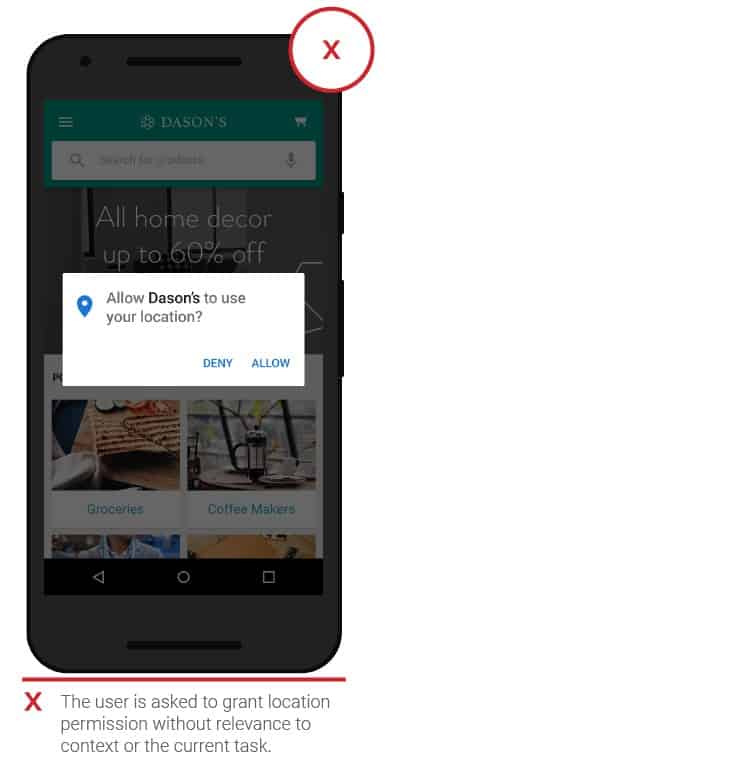
- Access request
When performing certain tasks, hitching may occur if access to functional parts of the system is not provided. Applications should request permission in a suitable situation. It is necessary to clarify the benefits of this. People are more likely to click the “allow” button if a request is made during the corresponding task.
Tools
The 25 mobile design principles outlined offer new solid insights into how to optimize the customer experience through streamlined navigation and search functionality, e-commerce design (conversions, signups, data entry forms), and quality usability.
Here are some useful tools that can help you achieve success throughout the lifecycle of your application:
- A strategy for increasing downloads will help you attract your audience. It’s worth taking a look at Google Recommendations: How to increase your mobile app downloads.
- Engage, expand and engage users with simple and reliable messages, regardless of the user’s platform (Android, iOS, or Chrome).
- 3. Remember to have an engagement strategy in place to retain your existing audience. Tools like external links and ad campaigns will help you with this.
- Grow your current customer base with Google App Invites.